vWork uses 3 sources to derive distance traveled
There are 3 sources that vWork uses to derive distance traveled. Each of these sources can be used to calculate mileage - a rate charged on a unit basis for distance traveled to complete a job. The source that is used for your account depends on the options enabled in your account.
The three sources are:
- Straight-line: This method calculates distance as an estimate based on a straight line between two points on a map. vWork adds together the straight line distance between all geocoded addresses from the steps in a job to calculate the total estimated distance. The straight-line method doesn’t use a route on a road network.
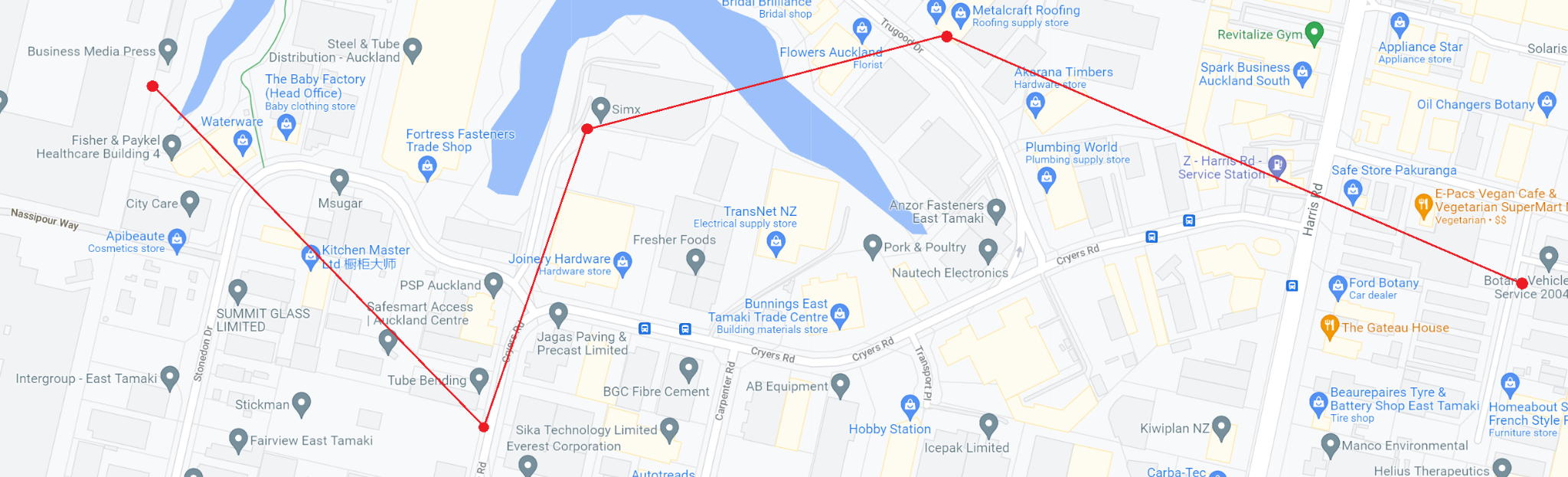
- Google Maps planned route:
This optional method calculates distance as an estimate based on the shortest Google Maps route between geocoded addresses from the steps in a job. The key difference between this and the straight-line method is that this method calculates distance on a turn-by-turn route following roads on google maps.
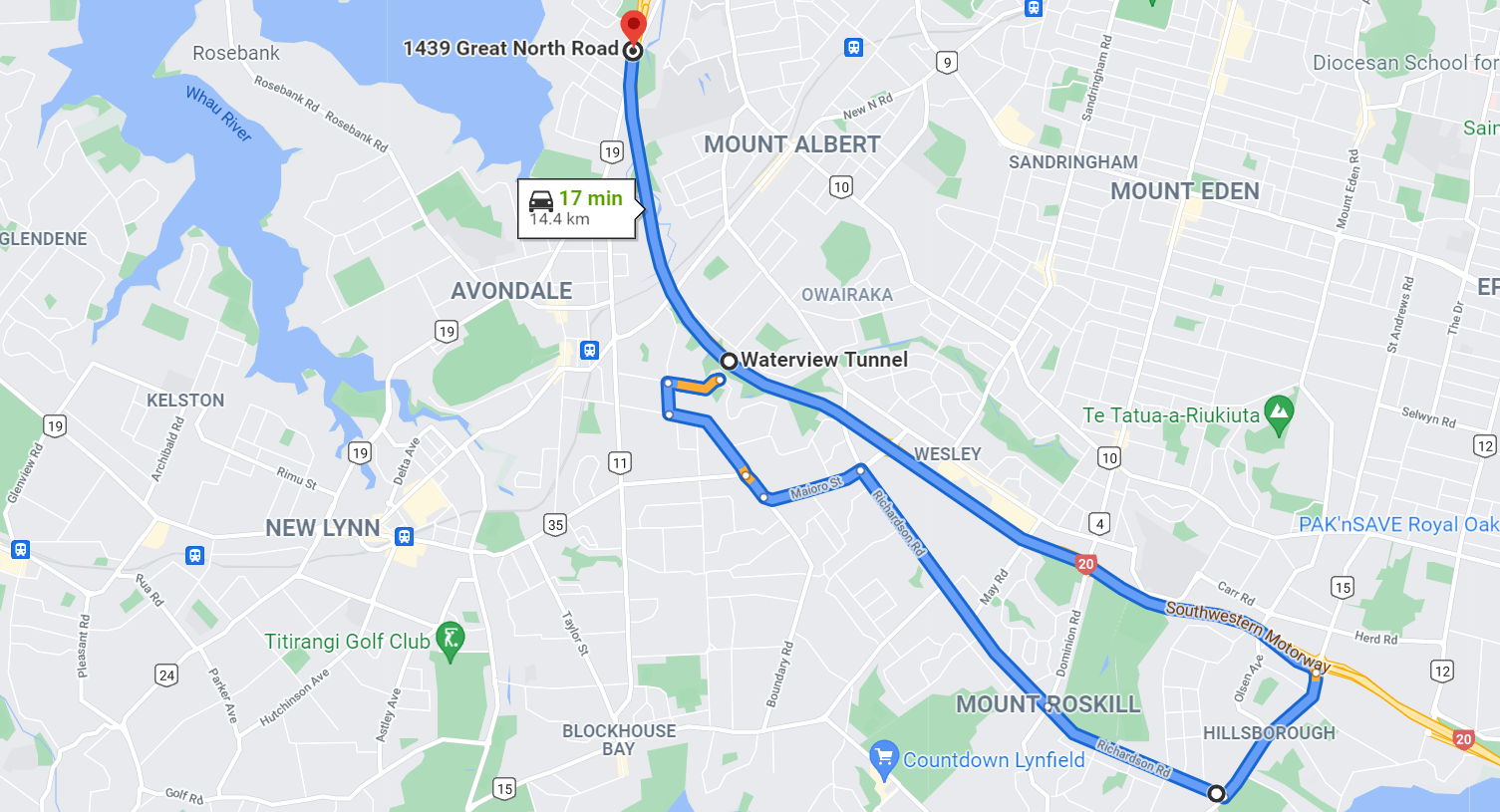
- EROAD actual mileage:
This optional method requires integration with EROAD. It uses the EROAD vehicle tracking device to provide actual distance traveled based on GPS information captured by the EROAD device between the job start time and the job completed time.
The key difference between this and the other two methods is that this provides actual, accurate distance. It is not an estimated distance. In addition, it does not use Geocoded addresses from the job because it tracks vehicle movement. To learn more about EROAD read Connect EROAD to vWork.
Tip: Google Maps routes and EROAD actual mileage can be used alongside each other in vWork for different purposes. For example, you can use Google Maps Route distance to prepare quotes and EROAD actual data on the final invoice.
Google Maps route and EROAD actual distance are vWork options. To enable either of these options in your account, please email support@vworkapp.com. A member of the vWork Team will be in touch to discuss your requirements.